| |
|
| What is DB-Migrator? |
| What is the need for DB-Migrator? |
| How DB-Migrator works? |
| |
| 1. Data Definition |
(i) How to Add a Table ?
(ii) How to Delete a Table ?
(iii) How to Add a Field ?
(iv) How to Delete a Field ?
|
| |
| 2. Data Mapping |
(i) What is data mapping ?
(ii) How to map data and migrate?
|
| |
| Definition:- |
|
| What is DB-Migrator? |
|
DB-Migrator is a tool that enables a lame user to perform
the following task on a database through simple steps:
- Create a database table.
- Extract data from another database table to the user created
tables.
- Frame rules for data extraction.
|
| Top |
|
| What is the need for DB-Migrator? |
|
For an application to produce the desired output, valid data
has to be entered into its database. The valid data can either
be entered manually or can be copied from another database.
Since each application maintains its data in its own comfortable
database (FoxPro, MS Access, MS SQL, Oracle etc), the process
of populating the database with the desired data is time consuming.
Invariably all businesses and enterprises use one or more
such custom applications for maintaining their business activity.
Each of these applications use specially tailored database
for maintaining its valuable data. If the enterprise plans
to go for a new application, the process of populating the
database of the newer application with the desired data is
time consuming.
The DB-Migrator provides an easy means of mapping the related
fields that has to be extracted from one database to another.
These data-mapping are saved as rules for performing the migration
operation in future.
|
| Top |
|
| How DB-Migrator works? |
|
The basic requirement for the DB-Migrator to work is the
Data Source Name (most commonly reffered as DSN), that points
to a database. If there is no DSN pointing to the source or
destination database, create a DSN pointing to the source
and destination database.
The migrator tool allows the user to select the source and
destination DSN. It displays all the tables available in that
database. The user has to select a source and destination
table and map the fields that has to be extracted to the destination
database. These map conditions are stored as rules for performing
data migration in the future.
It also offers a user the flexibility to create his own tables
and fields through another interface.
|
| Top |
|
|
Db-migrator consists of 2 section.
- Data Definition section.
- Data mapping section.
|
| 1. Data Definition is nothing
but defining tables, datafields, datafield type and datafield
size. |
Click on "Changes in DB (DDL)" Button to go to
the Data Definition form. The Data definition form is where
one can add or delete a table
|
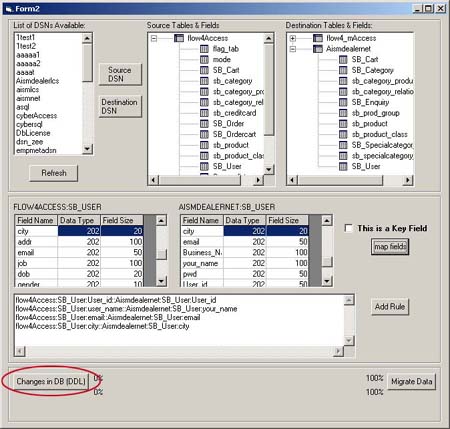 |
- Refresh Button gets available
system Data Source Name and populates the list List
of DSN Available.
- To select a DSN, double click a DSN from List
of DSN Available. A window pops up asking for username
and password required to access the database.
- The application tries connecting to the database using
the given username and password. If unable to connect, once
again asks for the user-name and password.
- On connecting to the database, the tables available in
that database are populated under Selected
DSNs.
- On selecting a table from Selected DSNs, the fields available
in that table are displayed under the Fields
list
|
| Top |
|
(i) How to Add a Table ?
|
Click on "Changes in DB (DDL)" Button to go
to the Data Definition form. The Data definition form
is where one can add or delete a table
|
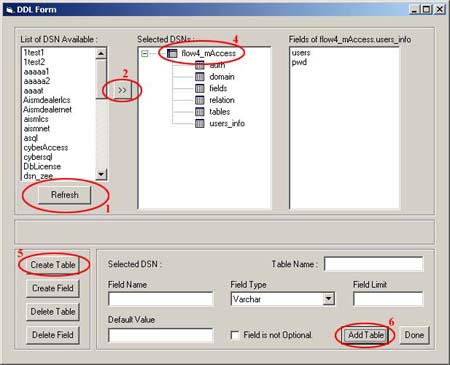
1. In the Data-Definition form, click on refresh button
to populate/refresh the available system Data-Source-Name.
2. Either Double-Click on the required DSN or select a
DSN and click the ">>" button.
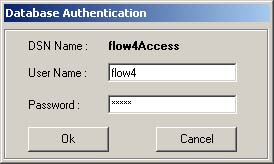
3. A window pops up asking for username and password to
connect to the database.
4. Select the DSN underwhich the new table has to be created
from the "Selected DSN's" list.
5. Click on "Create Table" button and enter
the following details:-
- Table Name
- Field Name
- Field Type
- Field size
- Default Value (optional)
- Is field required? (optional
6. Click on "Add Table" Button to add a table
with the above mentioned table name and field name.
|
 |
| |
 |
| |
| Top |
|
(ii) How to Delete a Table
?
|
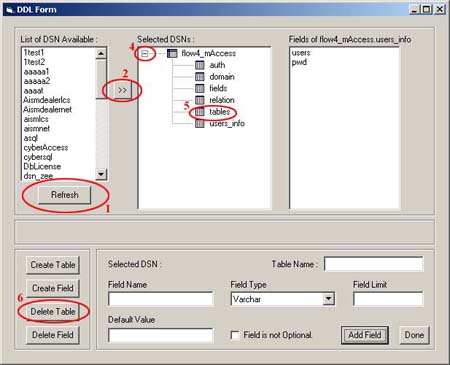
1. In the Data-Definition form, click on refresh button
to populate/refresh the available system Data-Source-Name.
2. Either Double-Click on the required DSN or select a
DSN and click the ">>" button.
3. A window pops up asking for username and password to
connect to the database.
4. Expand the list by clicking on the "+" sign
next to the DSN under "Selected DSN's" list.
5. Select the Table by clicking on its name from the list.
6. Click on "Delete Table" button. After a confirmation
message the table gets deleted from the database.
|
 |
| |
| Top |
|
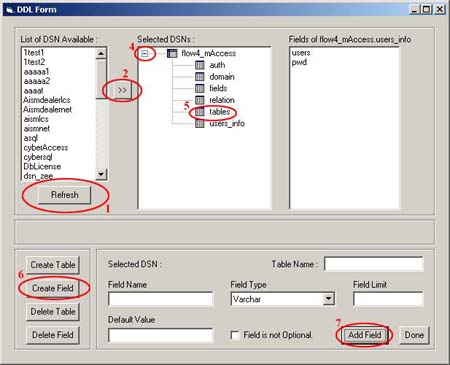
(iii) How to Add a Field ?
|
1. In the Data-Definition form, click on refresh button
to populate/refresh the available system Data-Source-Name.
2. Either Double-Click on the required DSN or select a
DSN and click the ">>" button.
3. A window pops up asking for username and password to
connect to the database.
4. Expand the list by clicking on the "+" sign
next to the DSN under "Selected DSN's" list.
5. Select the Table to which new fields are to be added.
6. Click on "Create Field" button and enter
the following details:-
- Field Name
- Field Type
- Field size
- Default Value (optional)
- Is field required? (optional
7. Click on "Add Table" Button to add a table
with the above mentioned table name and field name.
|
 |
| |
| Top |
|
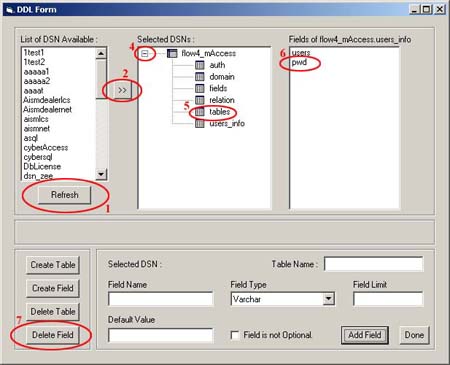
(iv) How to Delete a Field ?
|
1. In the Data-Definition form, click on refresh button
to populate/refresh the available system Data-Source-Name.
2. Either Double-Click on the required DSN or select a
DSN and click the ">>" button.
3. A window pops up asking for username and password to
connect to the database.
4. Expand the list by clicking on the "+" sign
next to the DSN under "Selected DSN's" list.
5. Select the Table in which fields are to be removed.
6. From the "Fields of DSN.TABLE" list select
the field that has to be removed
7. Click on the "Delete Field" button
|
 |
| |
| Top |
|
| 2. Data Mapping is where the
user maps fields from of one database to another. These relations
are stored as rules for extracting data from the source database
and for populating the destination databse. |
| |
(i) What is data mapping ?
|
Data mapping is a process by which the user specifies
what are the fields from a particular table has to be
exracted and placed in which table under which field.
|
| Top |
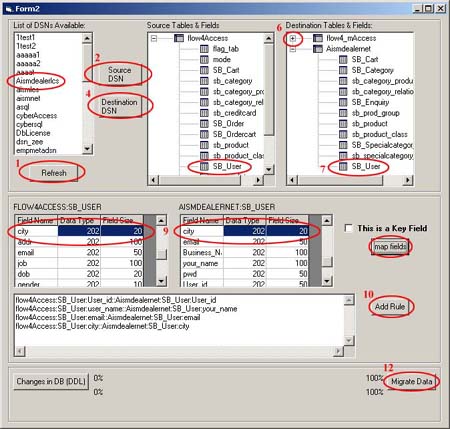
(ii) How to map data and migrate?
|
1. In the Data-Mapping form, click on refresh button
to populate/refresh the available system Data-Source-Name.
2. Select the DSN of the source database and click on
"Source DSN" button.
3. A window pops up asking for username and password to
connect to the database.
4. Select the DSN of the destination database and click
on "Destination DSN" button.
5. Supply the username and password in the window that
pops up.
6. Expand the list by clicking on the "+" sign
next to the DSN under "Source Tables" and "Destination
Tables" list.
7. Select source and destination table from the above
List.
8. Displays the available fields in the grid provided
below.
9. Select the matching fields and click on the "Map
Fields" button.
10. After mapping fields from a table save it as a rule
by clicking on "Add Rule" button
11. Repeat steps 7 to 10 for mapping fields in other tables.
12. Click on "Migrate Data" button to start
the data migration based on the above rules set by the
user.
|
 |
| |
| Top |
|
| Definition:- |
| Supported Data Types : Char, VarChar, LongVarChar,
SmallInt, Real, Float, Double, Numeric, SmallDateTime, DateTime |
| DSN : DSN (Data Source name) is used to identify a
data source or database on the network that is recognized from
the server. |
| Data Mapping : It is nothing but pointing a field in
a source table to a field in a destination table. Many such
mappings are grouped together to form a rule. |
| Data definition : It is the definition of how a table
should be, what are the fields it should contain and what should
be the length of each field. |
| |
|
Top
|
|
| |

